Both Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics are free tools provided by Google for webmasters or website owners to track their users. In this article, we will define & make a comparison of Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics. And we will also discuss the Benefits of both. Stay with SEO Focus Point.
Table of Contents
Importance of tracking and data analysis for websites
Before comparison of Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics, we have to know why will I track my website data. Tracking and data analysis play a crucial role in the success of websites for several reasons:
- Understanding User Behavior:
- Gain insights into how users interact with the website.
- Identify patterns, preferences, and pain points.
- Performance Optimization:
- Identify and resolve performance issues.
- Improve website speed, engagement, and conversions.
- Targeted Marketing and Personalization:
- Utilize data to create targeted marketing campaigns.
- Personalize experiences based on user demographics and preferences.
- Measuring Marketing Effectiveness:
- Evaluate the success of marketing efforts.
- Measure traffic sources, click-through rates, and conversions.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making:
- Make informed decisions based on objective data.
- Identify trends, opportunities, and areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement:
- Iterate and optimize website design and content.
- Conduct A/B tests and measure the impact of changes.
In summary, tracking and data analysis enables businesses to understand user behavior, optimize website performance, drive targeted marketing, measure marketing effectiveness, make data-driven decisions, and continuously improve their websites.
What is Google Tag Manager (GTM)?
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a free tag management system provided by Google. It simplifies the process of managing and deploying various tags, or snippets of code, on a website. These tags are typically used for tracking and collecting data for analytics, marketing, and other purposes.
Instead of manually editing website code to insert tags, GTM provides a user-friendly interface that allows users to add, update, and remove tags without directly modifying the underlying website code. It acts as a container that holds all the tags and provides a centralized platform for managing them.
GTM works by adding a single container code snippet to the website. Once the container is in place, users can set up and configure tags within GTM. This includes tags for tools like Google Analytics, Google Ads, Facebook Pixel, and more. GTM also provides triggers that determine when and where tags should fire based on specified conditions, such as page views, clicks, or form submissions.
The key benefits of using GTM include simplified tag management, streamlined deployment of tags without the need for code changes, version control to track and revert changes, and the ability to manage multiple tags from various providers in one place.
Overall, Google Tag Manager helps website owners and marketers efficiently manage and implement tags, making it easier to track website activity, collect data, and integrate with various analytics and marketing tools.
Benefits of using Google Tag Manager
Using Google Tag Manager (GTM) offers several benefits for website owners and marketers. Here are some key advantages:
Simplified Tag Management
GTM provides a user-friendly interface that simplifies the management of tags on a website. You can add, edit, and remove tags without directly modifying the website’s code, reducing reliance on developers and making the process more accessible to marketers.
Faster Deployment of Tracking Codes
With GTM, you can deploy tracking codes and tags quickly. Instead of manually inserting code snippets on every page, you can set up tags within GTM and have them applied site-wide or on specific pages with just a few clicks. This saves time and minimizes the risk of errors.
Version Control and Rollbacks
GTM offers version control, allowing you to keep track of changes made to tags and revert to previous versions if needed. This feature provides a safety net and allows you to easily troubleshoot issues or undo changes that may have negatively impacted your tracking or website performance.
Flexibility and Customization
GTM allows you to customize tags, triggers, and variables based on your specific tracking needs. You can define rules and conditions for when tags should fire, specify events to track and utilize variables for dynamic values. This flexibility enables more advanced tracking and customization options.
Streamlined Collaboration
GTM facilitates collaboration between marketing and development teams. Marketers can manage and implement tracking codes independently, reducing the dependency on developers for every tracking-related task. This streamlines the process, enhances productivity, and improves the efficiency of marketing campaigns.
Enhanced Performance and Site Speed
GTM loads tags asynchronously, which means they don’t block the rendering of web pages. This helps improve site speed and overall user experience. Additionally, GTM’s built-in load rules allow you to control when tags are triggered, minimizing any impact on page load times.
Integration with Third-Party Tools
GTM seamlessly integrates with various analytics and marketing platforms. You can easily add tags from tools like Google Analytics, Google Ads, Facebook Pixel, and more. This integration enables consolidated data collection, centralized management, and better insights into your website’s performance and marketing efforts.
In summary, the benefits of using Google Tag Manager include simplified tag management, faster deployment of tracking codes, version control, flexibility, and customization options, a streamlined collaboration between teams, enhanced site performance, and seamless integration with third-party tools. These advantages make GTM a valuable tool for efficient and effective website tracking and management.
Limitations of Google Tag Manager
While Google Tag Manager (GTM) offers several benefits, it’s important to be aware of its limitations. Here are some limitations to consider:
- Learning Curve: GTM has a learning curve, especially for users who are new to tag management systems. Understanding how to set up and configure tags, triggers, and variables requires time and familiarity with the GTM interface and terminology.
- Dependency on Internet Connection: GTM relies on an internet connection to load and deploys tags. If there are issues with the internet connection or if GTM servers experience downtime, it can impact the loading and functioning of tags on the website.
- Potential for Human Error: While GTM simplifies the tag management process, it still requires proper configuration. Misconfigurations or human errors in setting up tags, triggers, or variables can lead to incorrect data tracking or unintended consequences on the website.
- Limited Support for Advanced Functionality: While GTM provides flexibility, there may be instances where advanced tracking requirements or complex implementation scenarios are not fully supported. In such cases, additional customization or direct coding modifications may be necessary.
- Limited Control over Data Security: As a cloud-based service, GTM’s data security measures are largely managed by Google. This means that the control and management of sensitive data collected by tags within GTM may be subject to the policies and practices of the service provider.
- Impact on Website Performance: Although GTM aims to improve site performance, improper tag implementation or excessive use of tags can still have an impact on website speed. It’s crucial to ensure efficient tag management and regularly monitor website performance after implementing GTM.
- Limited Control in Highly Regulated Environments: In industries or organizations with strict data governance or regulatory requirements, there may be limitations on using third-party services like GTM for data collection and tracking. Compliance considerations should be carefully evaluated before implementing GTM.
It’s important to assess these limitations and consider whether GTM meets your specific requirements and aligns with your organization’s needs, security standards, and compliance regulations. Additionally, staying informed about updates and best practices for using GTM can help mitigate potential issues and maximize its effectiveness.
What is Google Analytics (GA)?
Google Analytics (GA) is an advanced web analytics tool offered by Google that provides website owners with detailed insights into their online presence. With GA, businesses can track and analyze various aspects of their website’s performance and user behavior.
By understanding visitor demographics, traffic sources, and browsing patterns, GA enables businesses to make data-driven decisions and optimize their online strategies. This powerful tool offers features such as conversion tracking, e-commerce analytics, customizable reports, and real-time reporting, allowing businesses to measure the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns, identify user preferences, and improve conversion rates. Moreover, GA seamlessly integrates with other Google services, providing a comprehensive view of marketing efforts across multiple platforms.
Overall, Google Analytics empowers businesses to understand their audience, enhance user experiences, and achieve their online goals through actionable insights and informed decision-making.
Benefits of using Google Analytics
Using Google Analytics offers numerous benefits for businesses and website owners. Here are some key advantages of implementing Google Analytics:
Data-driven Decision Making
Google Analytics provides valuable data and insights about website visitors, their behavior, and their interactions. This information enables businesses to make data-driven decisions, optimize marketing strategies, and improve overall website performance.
Audience Understanding
With Google Analytics, businesses gain a deeper understanding of their audience demographics, interests, and preferences. This knowledge helps tailor content, marketing campaigns, and user experiences to better meet the needs of the target audience.
Performance Tracking
Google Analytics allows businesses to track key performance metrics such as website traffic, conversion rates, bounce rates, and average session duration. This data helps identify areas for improvement, track marketing campaign effectiveness, and measure overall website performance.
Goal Tracking and Conversion Optimization
Businesses can set up goals and track conversions within Google Analytics. Whether it’s a purchase, form submission, or any other desired action, goal tracking helps measure and optimize conversion rates, identify bottlenecks, and improve website effectiveness.
Website Content Optimization
Through Google Analytics, businesses can analyze how visitors engage with different pages and content on their websites. This insight helps identify popular content, optimize underperforming pages, and enhance the overall user experience.
Campaign Performance Measurement
Google Analytics allows businesses to track the performance of various marketing campaigns, including paid advertising, email marketing, social media campaigns, and more. This data helps assess the ROI of different marketing initiatives and optimize marketing efforts accordingly.
Real-time Reporting
Google Analytics provides real-time reporting, allowing businesses to monitor website traffic, user behavior, and campaign performance in real time. This feature is valuable for time-sensitive campaigns, event tracking, and immediate data-driven decision-making.
Integration with Other Google Tools
Google Analytics seamlessly integrates with other Google tools such as Google Ads, Google Tag Manager, and Google Search Console. This integration provides a holistic view of online marketing efforts, enhances data analysis capabilities, and facilitates cross-platform tracking.
Cost-effective Solution
Google Analytics is a free tool with robust capabilities, making it a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes. It eliminates the need for expensive third-party analytics platforms and provides comprehensive insights at no additional cost.
In summary, Google Analytics empowers businesses with data-driven insights, audience understanding, performance tracking, conversion optimization, content optimization, campaign measurement, real-time reporting, integration with other Google tools, and cost-effectiveness. These benefits make Google Analytics a valuable tool for businesses seeking to optimize their online presence, drive growth, and improve marketing ROI.
Limitations of Google Analytics
Here are some limitations of Google Analytics in short points:
- Data Sampling: Google Analytics uses data sampling techniques for high-traffic websites, which can result in less accurate data representation for detailed analysis.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of Google Analytics involves the collection and processing of user data, which may raise privacy concerns and require compliance with data protection regulations.
- Data Attribution Challenges: Google Analytics uses last-click attribution by default, which may not accurately reflect the complete customer journey and give credit to all contributing marketing channels.
- Ad Blockers and JavaScript Dependency: Users with ad blockers or JavaScript disabled may not be tracked accurately or at all, leading to potential gaps in data collection.
- Limited Offline Tracking: Google Analytics primarily tracks online user interactions and may not provide comprehensive tracking for offline activities or interactions across different devices.
- Data Processing Delay: There can be a delay in data processing and reporting in Google Analytics, which means real-time data may not be immediately available for analysis.
- Lack of Individual User Identification: Due to privacy considerations, Google Analytics doesn’t provide detailed information on individual users, making it challenging to analyze behavior at a granular level.
- Limited Customization for Advanced Tracking: While Google Analytics offers customization options, more complex tracking requirements may require additional development or integration with other tools.
- Reliance on Google Services: Google Analytics relies on Google’s infrastructure, and any disruptions or outages in their systems can impact data collection and reporting.
- Learning Curve and Technical Expertise: Setting up and configuring Google Analytics effectively may require a learning curve and technical expertise, especially for advanced features and customization.
It’s important to consider these limitations while using Google Analytics and explore additional tools or techniques to address specific requirements or overcome these constraints if necessary.
Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics(Differences)
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics:
| Google Tag Manager (GTM) | Google Analytics (GA) | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Tag management system | Web analytics platform |
| Functionality | Manages and deploys tracking codes and tags | Tracks and analyzes website performance and data |
| Implementation | Requires adding GTM container code to the website | Requires adding GA tracking code to the website |
| Code Modification | No need to modify the website code directly | Requires manual modification of website code |
| Tag Deployment | Tags can be deployed and managed from the GTM interface | Tags are implemented directly within the website code |
| Flexibility | Offers flexibility and customization in managing tags, triggers, and variables | Limited customization options, primarily focused on analyzing website data |
| Collaboration | Facilitates collaboration between marketing and development teams | Primarily used by marketing teams, collaboration with developers may be required for code modifications |
| Tracking Options | Can track various third-party tags and scripts | Tracks website traffic, user behavior, conversions, and more |
| Real-Time Data | Provides real-time tag firing and debugging capabilities | Provides real-time reporting of website data |
| Learning Curve | Requires understanding of GTM interface and terminology | Requires understanding of GA interface and reporting metrics |
| Dependency | Dependent on GA for reporting and data analysis | Independent of GTM, can work with other analytics tools |
| Cost | GTM is a free tool provided by Google | GA has a free version, with additional paid features available |
It’s important to note that GTM and GA are often used together, with GTM handling the deployment of tracking codes and tags, while GA collects and analyzes the data. The combination of GTM and GA provides a comprehensive solution for managing website tracking and analyzing user behavior.
Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics(Similarities)
Here’s a table illustrating the similarities between Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics:
| Google Tag Manager (GTM) | Google Analytics (GA) | |
|---|---|---|
| Google Ecosystem | Part of the Google ecosystem | Part of the Google ecosystem |
| Data-Driven Insights | Provides data-driven insights | Provides data-driven insights |
| Website Tracking | Used for website tracking and management | Used for website tracking and analysis |
| Customization | Offers customization options | Offers customization options |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Provides real-time monitoring capabilities | Provides real-time reporting |
| Integration | Easily integrates with GA and other tools | Can be integrated with GTM for streamlined implementation |
Please note that while there are similarities between Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics, they serve different purposes and are designed to complement each other in the web analytics process.
Installation Process
Our topic is Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics. Both are very easy to install. Follow the step-by-step Guide:
Install Google Tag Manager
To begin using Google Tag Manager, the easiest approach is to locate the code and instructions within the Tag Manager interface. Here are the steps to get started:
Step 1: Go to the Google Tag Manager and sign in using your Google account. If you don’t have an account, you can create one for free.
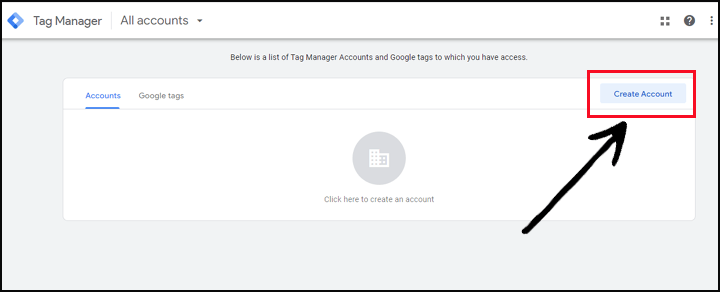
Step 2: Once you’re signed in, click on Create Account to set up a new container for your website. Enter an account name (usually your website or organization name) and select the target platform (web, iOS, Android).
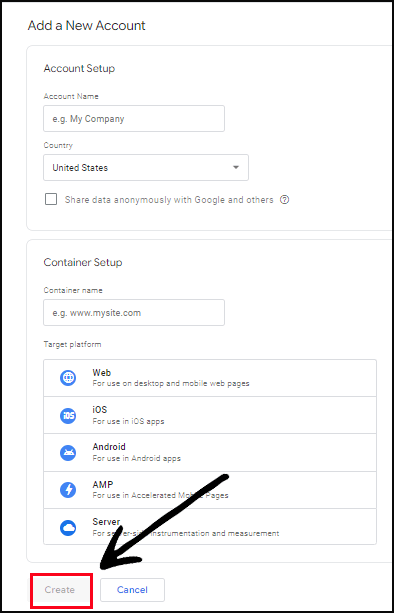
Step 3: After creating the container, you’ll see a page with the container snippet. This snippet is a combination of JavaScript code that needs to be placed on your website. There are two parts to the snippet: the “head” code and the “body” code.
Step 4: Copy the “head” code from the container snippet and paste it into the <head> section of every page on your website. This code should be placed immediately after the opening <head> tag.
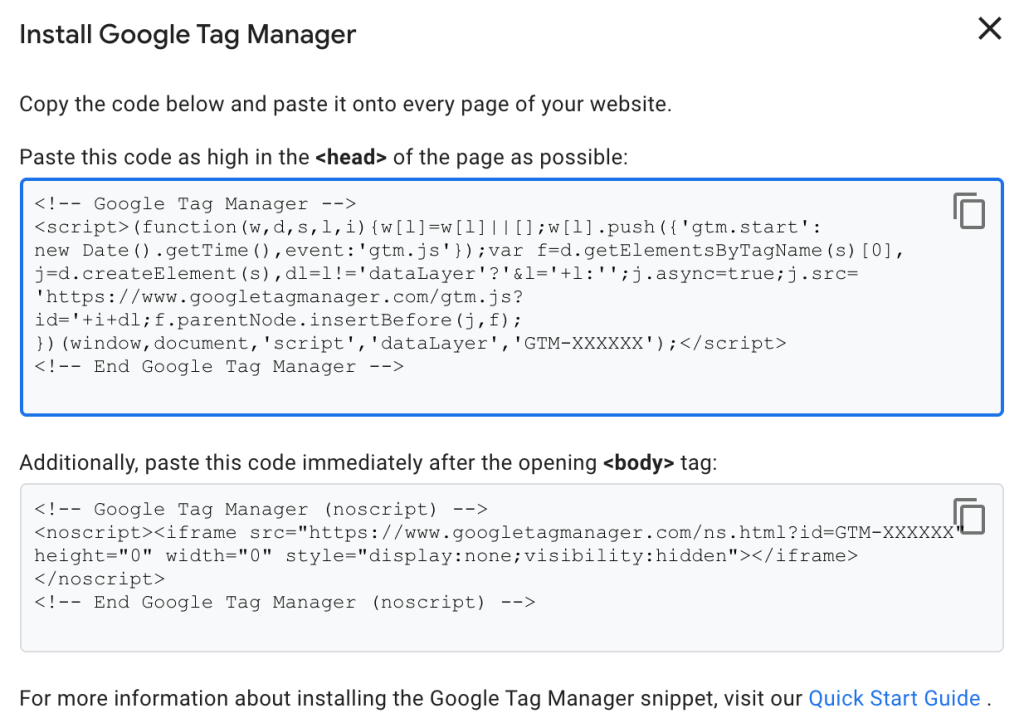
Source: Google Developers
Step 5: Implement the “body” code: Copy the “body” code from the container snippet and paste it into the <body> section of every page on your website. This code should be placed immediately after the opening <body> tag.
Step 6: Save the changes to your website’s code and publish it. This will activate the Google Tag Manager container on your website.
Step 7: After publishing the changes, go back to the Google Tag Manager interface and click on Submit in the top right corner. This will submit the container for publication. Once published, you can verify the installation by visiting your website and checking if the container is active.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Google Tag Manager on your website. You can now start adding tags, triggers, and variables to track and analyze various aspects of your website’s performance. Remember to test your tags and ensure they are firing correctly before relying on the data collected by Google Tag Manager.
Install Google Analytics
Here is the step-by-step guide for the installation of Google Analytics:
- Sign up for Google Analytics: Go to the Google Analytics website and sign in with your Google account. If you don’t have one, create a new account.
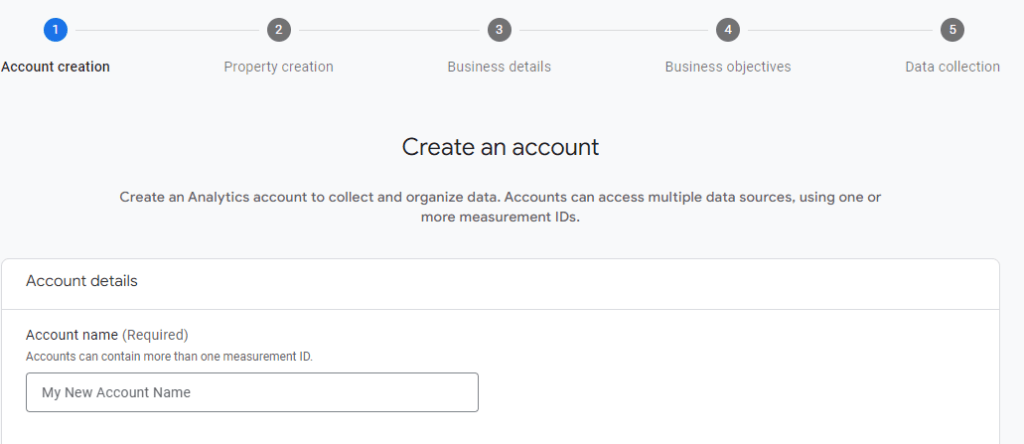
- Create a new property: Once you’re signed in, click on the “Admin” tab in the lower-left corner. In the “Account” column, click on the dropdown menu and select Create Account. Fill in the required details for your website, including the website name, URL, and industry category.
- Configure tracking settings: After creating the property, you’ll see a tracking code snippet. This code needs to be added to the pages of your website. There are two types of tracking codes: gtag.js and analytics.js. Choose the one that suits your needs and follow the instructions provided to install it.
- If you’re using gtag.js: Copy the code snippet and add it just before the closing </head> tag on each page of your website.
- If you’re using analytics.js: Copy the code snippet and add it just before the closing </body> tag on each page of your website.
- Verify installation: Save the changes to your website and access a few pages to ensure the tracking code is installed correctly. You can then go back to the Google Analytics interface and click on “Home” to see if data is being collected.
- Explore Google Analytics: Once your tracking code is installed and data is collected, you can start exploring the Google Analytics dashboard to gain insights into your website’s traffic, user behavior, and other metrics.
Remember, the specific steps may vary depending on your website platform or content management system (CMS).
Conclusion
Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics are powerful tools for tracking and analyzing website data. GTM simplifies tag implementation, while GA provides comprehensive analytics. There are also some differences and similarities between Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics. Join our newsletter to stay updated on data-driven strategies for website optimization. Unlock your website’s full potential today!