In the ever-evolving world of SEO, one question continues to spark debate: does content length truly matter for SEO and search engine rankings? Some say that “longer is better,” while others argue that quality trumps quantity. As digital marketers, we’re constantly looking for that sweet spot where content length and quality meet to deliver top-ranking results. But is there a magic number? Let’s dive deep into the relationship between content length and SEO to understand if length impacts rankings—and if so, how.
Table of Contents
Does Longer Content Rank Better?
There’s no shortage of studies suggesting that longer content often ranks higher in search engine results. For instance, a study by Backlinko found that the average word count of a first-page Google result is 1,447 words, Ahrefs analyzed over two million pages and discovered that content with a higher word count tends to outperform shorter articles in the SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages).

So what content seems to perform so well? For one, it offers more opportunities to incorporate a broader range of keywords naturally, increasing its relevance for various search queries. Longer articles also tend to keep users engaged for more time, contributing to metrics like “dwell time”—the amount of time a visitor spends on a page before returning to the search results. These engagement signals can indicate to search engines that users find the content valuable, which may contribute to higher rankings.
Quality vs. Quantity: Which is More Important?
Quality content has always been a cornerstone of SEO. Search engines like Google prioritize user experience, and high-quality content that provides value to readers is more likely to rank well. Here’s why quality is crucial:
- User Engagement: High-quality content that answers a user’s question or solves their problem keeps them engaged. If readers find your content useful, they are more likely to spend time on your page, reducing bounce rates and increasing dwell time—two important ranking signals for Google.
- Authority and Trust: High-quality content builds trust and authority. When you provide valuable information, supported by research, case studies, or examples, users perceive your site as an expert resource. This can lead to more backlinks, shares, and mentions—key factors in improving your domain authority (DA) and search engine rankings.
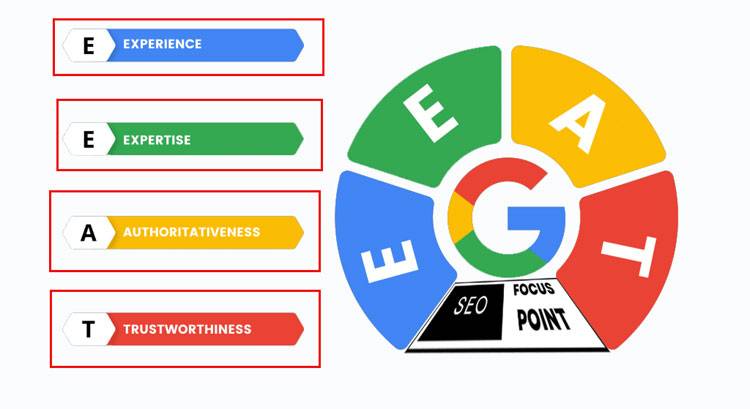
- Google’s Algorithms and E-E-A-T: Google’s algorithm has evolved to prioritize quality over sheer volume. It values content that aligns with its E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) guidelines. This means content must be factual, well-researched, and written by or attributed to experts in the field.
Actionable Tip:
Focus on delivering in-depth, well-structured, and thoroughly researched articles. Always aim to add value to the user’s experience, whether through actionable insights, original research, or expert opinions.
Content-Length by Type of Content
The ideal content length can vary significantly depending on the type of content you’re creating. Different content types serve different purposes, and each requires its approach to word count to effectively engage the target audience. Here’s a breakdown of content length recommendations based on various types of content:
Blog Posts and Articles
Blog posts and articles are one of the most common types of content, and their length can range from short, quick updates to in-depth guides. The key to determining the ideal word count is to focus on the intent behind the post and the complexity of the topic.
Short-Form Blog Posts (300–800 words)
These posts are often used for quick updates, news, or announcements. They are usually best for time-sensitive information or topics that don’t require much detail. While shorter blog posts can perform well in terms of engagement, they are less likely to rank for highly competitive keywords.
- Example: Industry news, product announcements, or event updates.
Standard Blog Posts (1,000–1,500 words)
These posts are ideal for moderately detailed topics. They provide enough room to explore a topic thoroughly without overwhelming the reader. Standard-length blog posts tend to rank well for mid-level keywords and are popular for “how-to” guides, listicles, and case studies.
- Examples: How-to guides, product reviews, and listicles.
Long-Form Articles (1,500–3,000+ words)
In-depth, long-form content often performs well in search engines because it provides comprehensive coverage of a topic. These articles can target more competitive keywords and offer value through thorough explanations, data, examples, and expert insights. Long-form articles are great for evergreen content and thought leadership pieces.
- Example: Ultimate guides, comprehensive tutorials, research-based articles.
Product Pages (300–500 words)
Product pages are critical for e-commerce websites, but they don’t require as much content as blog posts or articles. The primary focus is on providing clear, concise information that encourages conversions. That said, well-written product descriptions that are detailed enough to answer potential customer questions can help improve search visibility and rankings.
- Example: Product descriptions should include the key benefits, specifications, features, and any unique selling points of the product. User-generated content, like reviews and FAQs, can also add to the page’s length and relevance.
- Actionable Tip: Use bullet points, clear headings, and concise paragraphs to make the product information easy to scan while incorporating relevant keywords to improve search visibility.
Landing Pages (500–1,500 words)
Landing pages are designed to convert visitors into customers, subscribers, or leads. They often focus on a specific product, service, or offer and need to balance brevity with detailed information that persuades users to take action.
- Examples: Service pages, sales pages, or lead generation pages.
For landing pages, the ideal length depends on the complexity of what’s being offered. A short landing page might work well for a simple call-to-action like signing up for a newsletter, while a longer page may be needed to sell a more complex product or service.
- Actionable Tip: Use strong visuals, testimonials, and concise copy that builds trust. Keep the information relevant and focused on driving conversions. Test different page lengths using A/B testing to see what works best for your audience.
Pillar Pages and Resource Hubs (2,000–4,000+ words)
Pillar pages are designed to serve as comprehensive resources for a specific topic, often linking to related content within a website. These pages are highly valuable for SEO because they provide exhaustive coverage of a topic and can rank for a wide variety of keywords.
- Example: A pillar page on “SEO Basics” might cover various aspects like keyword research, link building, on-page SEO, and technical SEO, linking to more detailed blog posts on each subtopic.
Pillar pages are meant to be comprehensive, authoritative, and well-structured. Because they cover a broad topic in great depth, they tend to be much longer than typical blog posts.
- Actionable Tip: Include a table of contents, use clear headings for different sections, and make the page easy to navigate. The goal is to make it a go-to resource for readers and search engines alike.
Case Studies and White Papers (1,500–3,000 words)
Case studies and white papers are often used in B2B marketing to showcase a company’s expertise, success stories, and thought leadership. These content types are generally longer because they require detailed explanations, data, and analysis.
- Example: A white paper discussing the impact of AI on digital marketing may need to cover research data, insights, and actionable strategies, resulting in a higher word count.
- Actionable Tip: Use visuals like charts, graphs, and data tables to support your content and break up the text. Ensure that the writing is structured logically, guiding readers from problem to solution, backed by evidence and real-world examples.
Listicles (1,000–2,000 words)
Listicles, or “list posts,” are highly popular for their easy-to-read format and ability to cover a lot of ground in a structured way. The length of a listicle depends on the number of points and the depth of information covered for each item. Longer listicles (e.g., “Top 50 Digital Marketing Tools”) tend to rank better because they provide a broad range of options and insights.
- Example: “10 Best SEO Tools for 2024” or “25 Social Media Strategies for Small Businesses.”
- Actionable Tip: Each point in your listicle should be substantive. Use headings, short paragraphs, and images to keep the content scannable and engaging. Even though listicles can be long, they should never feel overwhelming due to their segmented structure.
User-Generated Content (Variable Length)
User-generated content (UGC) like reviews, comments, and forum posts can vary widely in length but offers immense SEO value. This type of content may be short, but it’s often seen as authentic and trustworthy, making it valuable for building credibility and engagement.
- Example: Customer reviews on an e-commerce website or comments on a blog post.
- Actionable Tip: Encourage user interaction by providing easy options for leaving reviews, asking questions, or contributing to discussions. While UGC doesn’t need to be long, its relevance and authenticity can help improve SEO by keeping the content fresh and engaging.
News Articles (300–800 words)
News articles typically aim to deliver timely information quickly and succinctly. Readers searching for news updates often prefer shorter, easily digestible pieces. However, in-depth investigative reports or opinion editorials may require more words.
- Example: Breaking news, event recaps, or press releases.
- Actionable Tip: Stick to the facts and keep the structure clear. Shorter paragraphs and bullet points can help readers quickly absorb the main points.
How to Determine the Right Content-Length for Your Website
Finding the ideal content length for your website isn’t as simple as following an industry average. You need to consider a few key factors:
- Understanding Your Audience’s Needs: Different audiences have different expectations. For instance, B2B readers may prefer in-depth, data-driven content, while B2C audiences might gravitate toward shorter, more engaging posts. Always create content that meets your audience’s needs.
- Competitor Analysis: Check out what’s ranking for your target keywords. If the top results are longer, detailed posts, it may indicate that comprehensive content is needed. SEO tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Surfer SEO can help you compare the average word count of top-ranking content in your niche.
Using SEO EO tools provides insights into your content’s ideal word count. These tools analyze search intent, top competitors, and ranking factors to suggest the appropriate content length to compete effectively.
Best Practices for Content-Length and SEO
Content length is undeniably an important consideration for SEO, but it must work in harmony with quality, relevance, and user experience. Simply extending the word count won’t guarantee higher rankings, especially if the content lacks substance or fails to address user intent. Here are some of the most effective best practices to help ensure your content length positively impacts SEO without sacrificing quality or usability.
Focus on Content Depth, Not Just Length
One of the biggest misconceptions in SEO is that longer content automatically ranks better. While longer articles tend to perform well in search rankings, this is often because they are more comprehensive, covering a topic in depth. Search engines like Google prioritize content that provides detailed answers to user queries, offering a holistic view of the subject.
- Actionable Tip: Instead of focusing on a specific word count, concentrate on fully answering the search query or topic at hand. Use content length as a byproduct of providing a well-rounded, informative piece that leaves the reader satisfied. For example, if you’re writing about “how to choose a running shoe,” cover all aspects—from foot types, and shoe categories, to material and pricing.
Match Content Length to Search Intent
Search intent is one of the most critical ranking factors, and Google is highly focused on delivering the most relevant results to users based on their queries. The length of your content should be driven by what the searcher is looking for. For example:
- Navigational searches: These typically require shorter, straightforward answers (e.g., finding a homepage or login page).
- Informational searches: Users might be looking for in-depth guides, FAQs, or how-tos, requiring longer, detailed content.
- Transactional searches: These involve product searches or purchase-related queries, where concise but compelling content that addresses user needs may perform best.
- Actionable Tip: Analyze the type of queries your target audience is using and create content that matches the intent behind those searches. For example, if the top-ranking pages for “how to start a blog” are over 2,000 words, it’s an indication that users want a thorough, step-by-step guide. On the other hand, a keyword like “buy running shoes” may lead to shorter, product-focused pages, where concise, conversion-driven content is ideal.
Prioritize Quality Over Quantity
While length is often correlated with rankings, quality remains the cornerstone of successful content. Adding unnecessary words or “fluff” just to meet a word count can hurt user engagement, leading to higher bounce rates and poorer user signals. Search engines are sophisticated enough to identify quality content based on factors like relevance, structure, and engagement.
- Actionable Tip: Every word should add value to the reader. Avoid stretching content with irrelevant or repetitive information. Instead, make sure your writing is clear, direct, and offers valuable insights. High-quality content naturally tends to be longer because it is more comprehensive and well-researched, but its main goal is to inform and engage users effectively.
Structure Content for Readability and Engagement
Long-form content is only effective if it is easy to read and navigate. Users tend to scan content rather than read every word, so a clear, scannable structure is essential for keeping them engaged. Proper formatting, including the use of headings, subheadings, bullet points, and images, can help break down information into digestible chunks and improve overall user experience.
- Actionable Tip: Use H2 and H3 headers to organize content into sections, making it easy for readers to jump to the part most relevant to them. Include short paragraphs and use bullet points or numbered lists to convey important information. Infographics, videos, and images can also enhance engagement by offering visual breaks or complementary explanations.
Optimize Content for User Engagement Metrics
Google pays attention to user engagement metrics like dwell time, bounce rate, and click-through rate (CTR), all of which signal how useful and engaging your content is. Longer content naturally has the potential to keep users on the page for longer periods, but it must maintain their interest to avoid high bounce rates.
- Actionable Tip: Keep users engaged by writing engaging introductions, using storytelling techniques, or asking questions that resonate with the reader. Incorporate internal linking to guide users to related content on your website, increasing dwell time. Use a mix of media—such as videos or interactive elements—to hold user attention and improve overall engagement.
Internal and External Linking
One advantage of longer content is the ability to naturally incorporate both internal and external links. These links not only enrich the content by providing additional context or resources but also enhance SEO by passing link equity (in the case of internal links) and signaling credibility (in the case of external links).
- Internal Links: These links guide users to other relevant content on your website, increasing session duration and improving site navigation. For instance, if you mention keyword research in a blog post, you can link to an existing detailed guide on that topic within your site.
- External Links: Linking to authoritative external sources can improve the credibility of your content. When citing statistics, studies, or research, be sure to link to trusted websites. This shows both users and search engines that you’ve done your homework and are providing well-researched, trustworthy content.
- Actionable Tip: Aim to include 3–5 internal links and 2–3 external links in long-form articles. Ensure that the links are relevant and add value to the user experience. Don’t overdo it—avoid adding links for the sake of SEO; they should feel natural and useful.
Balance Evergreen and Up-to-Date Content
For long-form content to consistently drive traffic, it should either be evergreen (content that remains relevant over time) or updated regularly. Long-form content is particularly suited to topics that offer lasting value. For instance, articles on “SEO best practices” or “How to create a content marketing strategy” can remain useful for years but may require occasional updates to stay relevant to industry changes.
- Actionable Tip: For evergreen content, create “cornerstone” articles that cover timeless topics in-depth. Regularly review and refresh these posts with updated information, stats, or trends to ensure their relevance. This signals to Google that your content is fresh and up-to-date, which can positively impact rankings.
Utilize SEO Tools for Content-Length Insights
SEO tools like Surfer SEO, SEMrush, and Ahrefs can provide insights into the optimal content length for a given keyword. These tools analyze the top-ranking content in your niche and give data-driven recommendations on the average word count required to compete. Such insights can help you avoid guessing the appropriate length and focus on creating content that is competitive in your market.
- Actionable Tip: Use these tools to analyze the SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages) for your target keyword. They provide recommendations based on competitors’ content length, structure, and keyword usage. Use these insights to balance word count with quality and relevance.
Encourage Engagement and Interaction
Longer content presents an opportunity to encourage reader interaction, which can positively influence SEO. Comments, shares, and social engagement not only boost visibility but also serve as signals of user satisfaction.
- Actionable Tip: End long-form content with a compelling Call-to-Action (CTA) that encourages readers to leave comments, ask questions, or share the post on social media. This not only fosters engagement but also sends positive user signals back to Google, further enhancing your content’s visibility in the SERPs.
Conclusion
Content length does matter for SEO, but it’s not the only thing that matters. Longer content can help you rank higher, especially if it allows you to dive deep into a topic, provide value, and satisfy search intent. However, the key to SEO success is creating high-quality content valuable to your audience—whether it’s 500 or 5,000 words long.
The next time you sit down to create content, don’t focus solely on word count. Instead, focus on how you can provide the most value to your audience and answer their questions better than anyone else. By doing that, you’ll see results in both your rankings and user satisfaction.


2 thoughts on “Content Length: Does It Really Impact SEO and Rankings in 2025?”