How to Do Technical SEO Step by Step? If you’ve ever wondered why your content isn’t ranking even though it’s packed with keywords and high-quality information, the answer might lie beneath the surface — in your technical SEO.
Technical SEO is like the foundation of a house. You can decorate your rooms (on-page SEO) and invite guests (off-page SEO), but if the structure isn’t solid, the whole thing could collapse. Simply put, technical SEO ensures that search engines can efficiently crawl, index, and rank your website.
To make technical and on-page SEO easier, I personally recommend using Surfer SEO. It offers real-time optimization suggestions based on top-performing pages, making it a powerful tool for beginners and experts alike.
For example, if your site loads slowly or isn’t mobile-friendly, Google may push you down the rankings. According to Google’s Page Experience update, factors like Core Web Vitals, mobile usability, and HTTPS directly influence your search visibility.
Or consider this: You wrote a killer blog post, but it’s buried under a poor site structure. Without a proper XML sitemap or internal linking, Googlebot might not even find it.
Many website owners and bloggers unknowingly miss out on traffic because they neglect this behind-the-scenes work. A study by Ahrefs found that 96.55% of content gets zero organic traffic from Google, and a large part of that is due to technical barriers.
But don’t worry — technical SEO doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step, beginner-friendly guide, you’ll learn how to:
-
Audit your site for crawlability issues
-
Optimize your website structure
-
Improve mobile-friendliness and site speed
-
Secure your site with HTTPS
-
Add structured data for better visibility
-
And much more…
We’ll also introduce some free tools (like Google Search Console, GTmetrix, and Screaming Frog) and real-world examples to help you understand and apply each step, even if you’re not a developer.
Whether you’re running a blog, a portfolio, or an eCommerce site, mastering technical SEO will set you up for long-term organic growth.
Table of Contents
🧱 What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimizing your website’s infrastructure so that search engines can crawl, index, and rank it more effectively. While on-page SEO focuses on content and keywords, and off-page SEO revolves around backlinks and authority, technical SEO ensures that your website is built to perform well in search engine algorithms.
Think of it this way:
Even the best content can’t rank if Google can’t access or understand it. Technical SEO lays the groundwork that allows your pages to shine.
🧠 Why Is Technical SEO Important?
Here are some compelling reasons why technical SEO is essential:

-
Improves Crawlability: Ensures search engines can access and navigate your content without hitting roadblocks.
-
Boosts Indexing: Helps search engines understand which pages to index — and which to avoid (like admin or thank-you pages).
-
Enhances Site Speed: Google considers fast-loading pages a ranking factor via Core Web Vitals.
-
Increases Mobile Usability: With mobile-first indexing, your site must perform well on smartphones and tablets.
-
Prevents SEO Issues: Fixes duplicate content, broken links, redirect chains, and other hidden errors that affect your rankings.
🔄 How Technical SEO Fits Into the Bigger Picture
To visualize how technical SEO works in tandem with other SEO elements:
| SEO Type | Focus Area | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| On-Page SEO | Content & user engagement | Keywords, meta tags, headings, images |
| Off-Page SEO | External signals | Backlinks, social shares, brand mentions |
| Technical SEO | Site infrastructure | Speed, mobile-friendliness, schema, indexation |
📌 Examples of Technical SEO in Action
-
A large e-commerce site with thousands of products uses XML sitemaps to ensure Google indexes all product pages.
-
A blogger notices high bounce rates and uses PageSpeed Insights to optimize images and reduce server load time.
-
A local business website adds structured data (schema) to appear with review stars and location info in SERPs.
-
A site audit reveals that 30% of URLs are returning 404 errors. The webmaster implements 301 redirects and sees ranking recovery.
In short, technical SEO is the foundation of your website’s search performance. Without it, even your best content might never reach your audience.
🧱 Step 1: Crawl Your Website
Before you can fix anything, you need to know what’s broken — and that’s where website crawling comes in. Crawling is the process search engines use to discover and analyze your website’s content and structure. If your site has broken links, inaccessible pages, or poor navigation, crawlers like Googlebot may not properly index your content — meaning you lose visibility in search results.
🔎 What Does It Mean to “Crawl” a Website?
When you perform a site crawl, you’re mimicking how Google and other search engines explore your pages. Crawling helps you detect:
-
Broken links (404 errors)
-
Redirect loops
-
Orphaned pages (pages with no internal links pointing to them)
-
Duplicate content
-
Missing meta tags or canonical tags
🛠️ Tools to Crawl Your Website
You don’t need to be a developer to run a website crawl. Here are some beginner-friendly tools:
| Tool | Description | Free Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | View crawl stats, indexing issues, and sitemaps | ✅ Yes |
| Screaming Frog SEO Spider | Desktop-based crawler to analyze your entire site | ✅ Up to 500 URLs |
| Ahrefs Site Audit | Detailed audit with health score and issue prioritization | ❌ Paid |
| Sitebulb | Visual SEO audits and crawl data | ✅ Free trial |
✅ How to Crawl Your Site (Step-by-Step with Screaming Frog)
-
Download and install Screaming Frog SEO Spider
-
Enter your domain URL (e.g.,
https://www.yoursite.com) and hit “Start” -
Wait while the tool scans your site — this may take a few minutes, depending on your size
-
View key reports:
-
Response Codes→ Find 404s and redirects -
Page Titles,Meta Descriptions→ Check for duplicates or missing data -
Directives→ See if important pages are blocked byrobots.txtornoindextags
-
💡 Pro Tip: Use Google Search Console’s “Coverage” report to find crawl errors directly from Google’s crawler, including Excluded URLs, Blocked by robots.txt, and Server Errors.
🧩 What to Do After the Crawl
-
Fix broken links: Redirect them or update internal links
-
Update meta tags: Add missing or duplicate titles and descriptions
-
Check indexability: Make sure important pages are indexable
-
Ensure correct redirects: Use 301 (permanent) instead of 302 (temporary) when needed
🧱 Step 2: Optimize Your Site Structure
A well-organized website structure is like a map — it helps both users and search engines easily find what they’re looking for. When your site structure is logical and clean, Googlebot can crawl and index your pages more effectively, and users can navigate your site without getting lost.
📚 What Is Site Structure in SEO?
Site structure refers to how your website’s content is organized and interconnected. This includes:
-
The hierarchy of pages (home → category → subcategory → content)
-
Internal linking between pages
-
URL structure (e.g.,
yoursite.com/blog/seo-basics) -
Breadcrumbs and navigation menus
✅ Why It Matters for SEO
A strong site structure:
-
Improves crawl efficiency and indexation
-
Helps pass link equity through internal links
-
Enhances user experience (UX)
-
Prevents keyword cannibalization
-
Creates opportunities for sitelinks in search results
📊 Google’s own documentation highlights that sites with a clear hierarchy are easier to crawl and rank better over time.
🛠️ How to Build an SEO-Friendly Site Structure (Step-by-Step)
1. Create a Clear Hierarchy
Structure your site like a pyramid:
Top level: Homepage
Second level: Main categories or services
Third level: Individual blog posts or product pages
💡 Example:
2. Use SEO-Friendly URLs
Keep URLs short, readable, and keyword-rich.
✅ Good: example.com/seo/technical-seo-checklist
❌ Bad: example.com/post?id=4321&ref=blog2025
3. Implement Internal Linking
Link related articles or product pages using descriptive anchor text.
For example, in a blog post about keyword research, link to your On-Page SEO Checklist using anchor text like:
👉 “Be sure to check out our On-Page SEO Checklist for optimization tips.”
4. Add Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumbs show users (and Google) where they are on your site.
Example: Home > Blog > Technical SEO > How to Crawl Your Website
They also enhance your listing in Google’s SERPs with navigational links.
5. Submit an XML Sitemap
A sitemap tells Google where all your important pages are. You can create one using tools like:
Submit your sitemap in Google Search Console under Index > Sitemaps.
🚫 Avoid These Common Mistakes
-
Having deep page levels (more than 3 clicks from the homepage)
-
Using inconsistent or irrelevant internal links
-
Letting orphaned pages (pages with no internal links) accumulate
-
Duplicating URLs due to tracking parameters or improper redirects
⚡ Step 3: Improve Mobile Usability and Site Speed
In today’s mobile-first world, your website must be fast and responsive, or risk losing both users and rankings. Since Google switched to mobile-first indexing, it now primarily uses the mobile version of your site to evaluate and rank your content.
A slow, clunky, or unresponsive mobile experience can result in:
-
Higher bounce rates
-
Lower engagement
-
Poor Core Web Vitals
-
Drops in search visibility
📱 Mobile Usability: Why It Matters
More than 60% of all web traffic comes from mobile devices. Google wants to ensure users have a smooth experience on smaller screens. That’s why mobile-friendliness is a ranking factor.
Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to check your site. It will flag issues like:
-
The text is too small to read
-
Clickable elements are too close together
-
Viewport not set properly
✅ Quick Fixes:
-
Use a responsive design that adapts to all screen sizes.
-
Increase font size to at least 16px for body text.
-
Use touch-friendly buttons and spacing.
-
Avoid popups or interstitials that block content.
🚀 Site Speed: Key for Rankings and UX
Google emphasizes page speed as part of its ranking system, especially through Core Web Vitals, which measure real-world user experience.
| Core Web Vitals | What It Measures | Ideal Value |
|---|---|---|
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | Loading performance | < 2.5 seconds |
| FID (First Input Delay) | Interactivity | < 100 ms |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | Visual stability | < 0.1 |
Run your site through PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to get a performance score and recommendations.
🛠️ Tips to Improve Speed & Mobile UX
-
Compress images using tools like TinyPNG or WebP format
-
Minify CSS, JS, and HTML
-
Use lazy loading for images and videos
-
Enable browser caching and GZIP compression
-
Choose a reliable web hosting provider
-
Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network) like Cloudflare for faster global loading
If you’re using WordPress:
-
Install plugins like WP Rocket, LiteSpeed Cache, or W3 Total Cache
-
Use lightweight themes like GeneratePress or Astra
💡 Pro Tip:
Google Search Console’s “Core Web Vitals” report (under the “Experience” tab) shows exactly which URLs are failing and why — broken down by mobile and desktop.
🧭 Step 4: Ensure Proper Indexing and Use of Robots.txt
Making your site accessible to users is one thing, but making it accessible to search engine bots is critical for SEO success. If Google can’t crawl and index your pages, they won’t appear in search results, no matter how good your content is.
This step focuses on ensuring that your most important pages are indexable and that unnecessary or sensitive pages stay hidden.
🧠 What Is Indexing?
Indexing is the process by which search engines store and organize the content they discover during crawling. If your page is not indexed, it cannot rank in search results.
You can check a page’s indexing status in Google Search Console (GSC) under:
Index → Pages → View Indexed/Not Indexed URLs
Or, simply search on Google:
If no result appears, it likely isn’t indexed.
📄 Use of Robots.txt and Meta Tags
✅ robots.txt – Controls crawling
This is a file placed at the root of your site (yourdomain.com/robots.txt) that tells search engines what they can and can’t crawl.
Example robots.txt:
⚠️ Don’t block CSS/JS files — it can hurt indexing and mobile usability.
✅ Meta Robots Tags – Controls indexing
Placed in the <head> section of a page, meta robots tags tell bots if a page should be indexed or followed.
Common values:
-
index, follow(default – allow everything) -
noindex, follow(don’t index the page, but follow its links) -
noindex, nofollow(don’t index the page or follow links)
🔎 How to Ensure Proper Indexing (Step-by-Step)
-
Check Your Robots.txt
-
Make sure important pages aren’t accidentally disallowed
-
Use Canonical Tags
-
Prevent duplicate content issues by specifying the “main version” of a page:
-
-
Inspect Pages in Google Search Console
-
Use the URL Inspection Tool to test how Google sees a page
-
See crawl status, indexability, canonical URL, and mobile usability
-
-
Submit a Sitemap
-
A well-structured XML sitemap helps Google discover all relevant pages quickly
-
-
Avoid Orphan Pages
-
Pages that have no internal links pointing to them are hard for search engines to find
-
Use tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs Site Audit to detect them
-
⚠️ Common Indexing Mistakes
-
Blocking important sections in robots.txt (e.g.,
/blog/) -
Adding
noindexby mistake (especially after redesigns or dev testing) -
Not submitting a sitemap in Google Search Console
-
Forgetting to remove password protection or staging site tags like
noindex, nofollow
🔐 Step 5: Secure Your Website (HTTPS) and Fix Crawl Errors
Security isn’t just important for protecting your users — it’s a confirmed ranking signal in Google’s algorithm. If your website still uses HTTP instead of HTTPS, you’re sending negative trust signals to both users and search engines.
Crawl errors, on the other hand, block search engines from accessing or understanding your content, causing major SEO issues if left unchecked.
🔒 Why HTTPS Matters in Technical SEO
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the data exchanged between your server and a user’s browser, protecting it from tampering and eavesdropping.
Google made HTTPS a ranking factor in 2014 and began labeling non-HTTPS sites as “Not Secure” in Chrome.
✅ Benefits of HTTPS:
-
Trust and credibility for users
-
Improved SEO performance
-
Required for AMP, Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), and Core Web Vitals
-
Enables secure shopping and form handling
🛠️ How to Switch to HTTPS (If You Haven’t Already)
-
Buy an SSL Certificate
-
Most web hosts now offer free SSL via Let’s Encrypt or paid options for advanced needs.
-
-
Install the Certificate via Hosting
-
Use your hosting provider’s control panel or ask for help.
-
-
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
-
Use 301 redirects from all
http://versions tohttps://to avoid duplicate content.
-
-
Update Internal Links
-
Change all hardcoded internal links to use
https://.
-
-
Re-submit Your Sitemap
-
Ensure Google indexes the secure version via Google Search Console.
-
🕵️♂️ Fix Crawl Errors in Google Search Console
Crawl errors prevent search engines from accessing your pages and waste crawl budget. Regularly audit and fix these issues to maintain healthy indexability.
🔍 Use GSC → Pages → Why pages aren’t indexed
Common crawl issues include:
-
404 Not Found
-
Server (5xx) Errors
-
Redirect Loops
-
Soft 404s
-
Blocked by robots.txt
🛠️ How to Fix:
-
404s → Redirect to a relevant page or update broken links
-
5xx errors → Check server configuration or hosting issues
-
Blocked pages → Adjust
robots.txtor meta robots tags -
Soft 404s → Add meaningful content or redirect/remove the page
You can also use tools like:
-
Screaming Frog SEO Spider
-
Ahrefs Site Audit
-
SEMrush Audit Tool
💡 Pro Tip:
Set up Google Alerts or Uptime Robot to monitor site downtimes and major crawl issues automatically.
🔗 Step 6: Improve Crawlability and Internal Linking
Even the best content can’t rank if search engines can’t find it. That’s where crawlability and internal linking come in. Think of these as your website’s roadmap — guiding both users and search engines to the most important pages.
If your site has poor internal linking or an unclear crawl path, important pages might be:
-
Ignored or never crawled
-
Indexed less frequently
-
Treated as low-priority
🕸️ What Is Crawlability?
Crawlability refers to how easily search engine bots (like Googlebot) can access and navigate your website. When bots crawl your site, they follow links to discover new content.
📋 How to Improve Crawlability (Step by Step)
-
Submit an XML Sitemap
-
Ensure it’s updated, error-free, and submitted in Google Search Console.
-
Include only index-worthy URLs.
-
-
Use a Flat Site Architecture
-
Structure your site so any page is accessible within 3 clicks from the homepage.
-
-
Avoid Deep Nesting
-
Avoid excessive subfolder levels like:
-
-
Limit Redirect Chains
-
Too many redirects waste crawl budget and slow down bots.
-
Fix redirect chains or loops using Screaming Frog or Ahrefs.
-
-
Fix Broken Links
-
Use tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, or Broken Link Checker to identify and remove/fix 404 links.
-
🔄 Internal Linking: Why It’s a Technical SEO Power Move
Internal links:
-
Pass link equity (SEO value) between pages
-
Help bots understand your site hierarchy
-
Improve crawl depth and indexation
-
Enhance user experience and reduce bounce rates
✅ Best Practices for Internal Linking:
-
Link from high-authority pages (like your homepage) to new or important content
-
Use descriptive anchor text (avoid “click here” or “read more”)
-
Add internal links contextually within the content, not just in footers or sidebars
-
Update old posts with links to new relevant content
-
Use breadcrumb navigation for better site structure
🧠 Bonus Tip:
Use a hub-and-spoke model:
-
Create a central “pillar” page targeting a broad topic.
-
Link out to detailed blog posts (“spokes”) covering subtopics.
-
Each spoke should also link back to the pillar page.
This helps build topical authority and strengthens your SEO.
🧩 Step 7: Implement Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Want to stand out in search results with star ratings, FAQs, or event dates? That’s where structured data, also known as schema markup, becomes a technical SEO superpower.
Structured data helps search engines understand the context of your content — not just the text on the page. It enhances your visibility with rich results that can improve click-through rates.
🤖 What Is Schema Markup?
A schema is a standardized format of code (usually in JSON-LD) that tells search engines what your content is about.
For example:
-
A blog post = Article
-
A recipe = Recipe
-
A product = Product
-
A review = Review
Structured data is not visible to users but is read by search engines to enhance listings with rich snippets.
⭐ Examples of Rich Results from Schema
| Schema Type | Rich Result Feature |
|---|---|
| Article | Image, headline, publish date |
| Product | Price, availability, reviews |
| FAQ | Expandable question boxes |
| Review | Star ratings |
| Event | Date, time, location |
| Recipe | Cook time, ingredients, rating |
🔍 Try searching for:
“chocolate cake recipe” — notice how some results show cook time, rating, and ingredients.
🛠️ How to Add Structured Data (Step-by-Step)
-
Choose the Right Schema Type
-
Visit Schema.org to find relevant schema types.
-
-
Use a Schema Generator
-
Tools like Merkle Schema Generator or Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper simplify this.
-
-
Insert the JSON-LD Code into Your HTML
-
Place it in the
<head>or just before the closing</body>tag.
Example for Blog Article:
-
-
Validate the Code
-
Monitor in Search Console
-
Go to Enhancements to see how your schema is performing and fix issues if needed.
-
⚠️ Pro Tips:
-
Only mark up content visible to users — don’t try to game the system.
-
Don’t overdo it. Focus on relevant schema types.
-
Combine schema types when appropriate (e.g., Product + Review).
📱 Step 8: Optimize for Mobile and Core Web Vitals
More than 60% of web traffic comes from mobile devices. And with Google’s mobile-first indexing, your site’s mobile version is the one that gets evaluated for ranking, not the desktop version.
Couple that with Core Web Vitals, and you’ve got a big chunk of technical SEO success riding on mobile performance and user experience.

📲 What Is Mobile-First Indexing?
Since 2019, Google has primarily used the mobile version of a site for indexing and ranking. This means:
-
Your mobile site must contain the same content and metadata as your desktop site.
-
Mobile usability issues can directly affect your rankings.
-
Fast loading times and good UX on mobile are essential.
🧪 How to Test Mobile Usability
-
Use Google Search Console → Mobile Usability Report
-
Find pages with text too small, clickable elements too close, or content wider than the screen.
-
-
Try Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test
👉 https://search.google.com/test/mobile-friendly -
Use Chrome DevTools → Device Toolbar
-
Simulate mobile view on desktop and test responsiveness.
-
🚦 What Are Core Web Vitals?
Core Web Vitals are a set of three performance metrics Google uses to measure user experience:
| Metric | Description | Ideal Score |
|---|---|---|
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | Measures load speed | < 2.5 seconds |
| FID (First Input Delay) | Measures interactivity delay | < 100 milliseconds |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | Measures visual stability (avoid content shift) | < 0.1 |
📌 Note: FID has been replaced with INP (Interaction to Next Paint) in 2024 as the primary interactivity metric.
🛠️ How to Optimize for Core Web Vitals
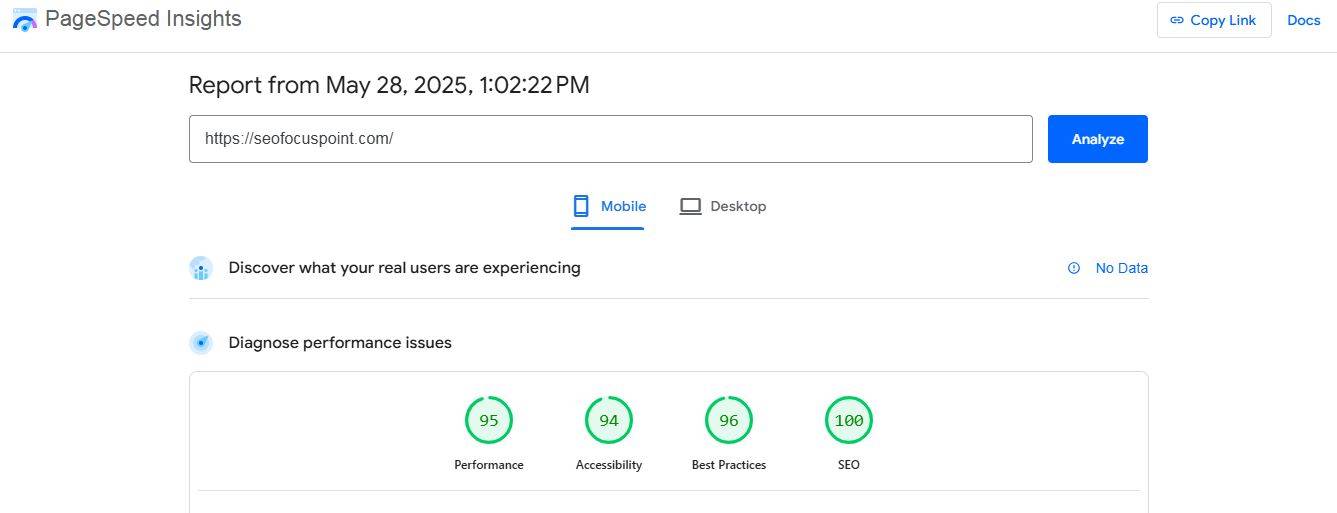
✅ 1. Improve LCP
-
Use fast hosting and a CDN
-
Optimize images (compress, use WebP)
-
Minify CSS/JS and remove unused code
-
Preload important assets
✅ 2. Improve INP (was FID)
-
Reduce JavaScript execution time
-
Minimize third-party scripts
-
Defer non-critical JS
✅ 3. Improve CLS
-
Always include width/height attributes on images and videos
-
Avoid inserting content above existing content (like banners)
-
Use reserved space for ads
⚙️ Tools to Measure & Monitor Core Web Vitals
-
PageSpeed Insights – https://pagespeed.web.dev/
-
Lighthouse in Chrome DevTools
- Surfer SEO
-
Web Vitals Extension for Chrome
-
Google Search Console → Core Web Vitals Report
-
Cloudflare or NitroPack for automated performance enhancements
💡 Bonus Tip:
Consider implementing AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) for lightning-fast mobile experiences, especially for content-heavy websites like blogs or news.
📊 Step 9: Monitor & Maintain Technical SEO Health
Technical SEO isn’t a one-and-done task — it requires ongoing attention and regular audits to keep your site in peak condition. Search engines and web technologies constantly evolve, so staying proactive is key.
🛡️ Why Monitoring Technical SEO Matters
-
Catch new crawl errors or indexing issues early
-
Detect performance drops or mobile usability problems
-
Keep your site secure and compliant with best practices
-
Ensure your structured data is valid and up to date
🔧 Tools to Regularly Monitor Your Technical SEO
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Crawl errors, indexing status, mobile usability, Core Web Vitals, structured data reports |
| Google Analytics | User behavior, bounce rates, traffic trends |
| Screaming Frog SEO Spider | Comprehensive site audits, broken links, redirects, duplicate content |
| Ahrefs / SEMrush Site Audit | Backlink health, site audit, on-page SEO issues |
| PageSpeed Insights / Lighthouse | Performance and Core Web Vitals |
| Uptime Robot / Pingdom | Monitor site uptime and downtime |
🔄 How Often to Audit?
-
Weekly: Check Google Search Console for critical errors
-
Monthly: Run full site audits with Screaming Frog or SEMrush
-
Quarterly: Review Core Web Vitals and mobile usability reports
-
After Major Changes: Always re-audit after site redesigns, migrations, or big content updates
🧹 Routine Technical SEO Maintenance Tasks
-
Fix broken links and 404 errors promptly
-
Update outdated or broken redirects
-
Keep your sitemap and robots.txt files updated
-
Refresh and validate structured data after content changes
-
Monitor site speed and optimize assets regularly
-
Ensure SSL certificates remain valid and renewed
📈 Pro Tip:
Set up automated reports and alerts where possible. For example, Google Search Console can email you critical issue notifications. Third-party tools like SEMrush can schedule audits and send summaries.
Conclusion
Mastering technical SEO step by step empowers your website to be easily discovered, trusted, and ranked by search engines. With strong foundations and ongoing care, your site’s visibility and user experience will steadily improve, fueling long-term SEO success. Don’t forget to subscribe our newsletter to get latest update of seo.

